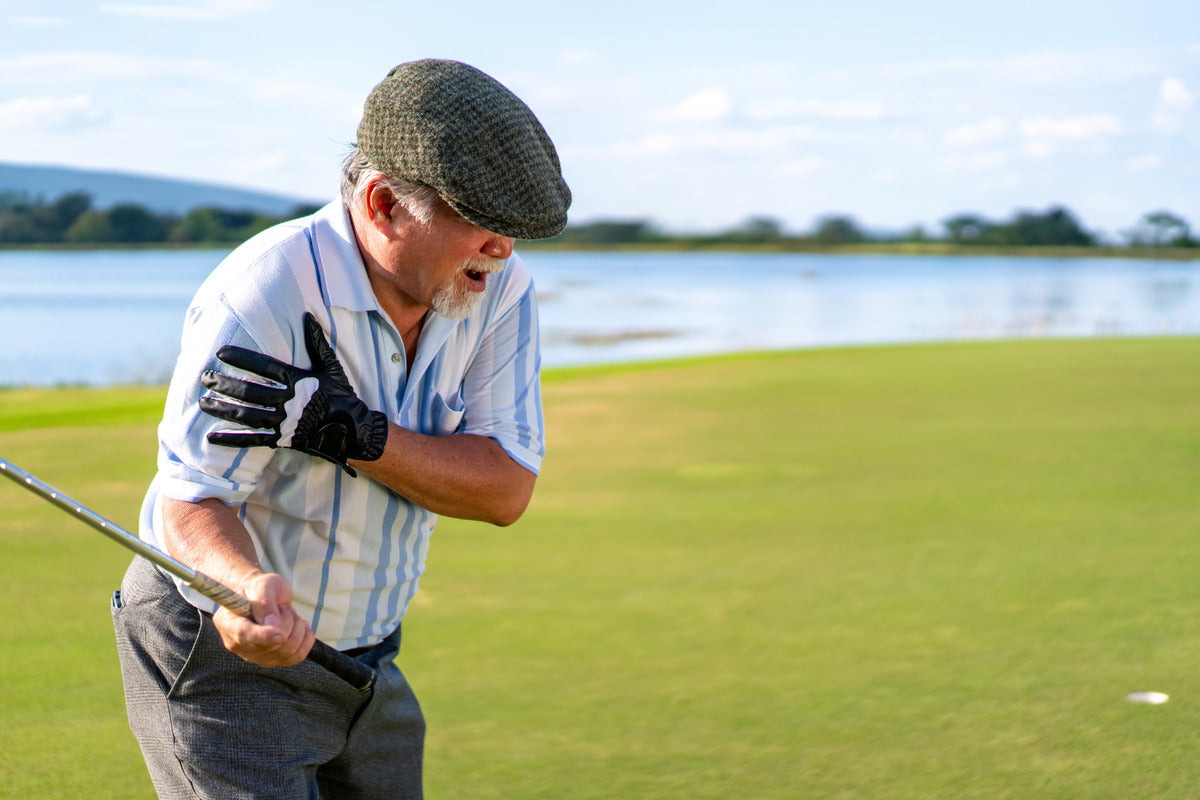
A Comprehensive Guide on Treating and Preventing Rotator Cuff Injuries
Rotator Cuff Injuries
Rotator cuff injuries are common, especially among athletes and those engaged in repetitive overhead activities. Understanding the types, causes, treatments, and preventive measures is crucial for maintaining shoulder health and avoiding long-term issues. In this blog, we'll delve into the intricacies of rotator cuff injuries, explore innovative treatments like peptides, and provide tips on prevention and shoulder pain relief.
Types and Common Causes of Rotator Cuff Injuries
Types of Rotator Cuff Injuries
- Tendinitis: This is the inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons, usually caused by repetitive overhead activities or overuse.
- Bursitis: Involves inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac that reduces friction in the shoulder.
- Rotator Cuff Tear: Tears can be partial or complete and occur in one or more of the rotator cuff tendons. These are often the result of acute injuries or degenerative changes.
Common Causes
- Overuse: Frequent overhead activities, heavy lifting, or repetitive shoulder movements are the most common causes of a rotator cuff tear.
- Acute Injury: Sudden injuries like falling on an outstretched arm, lifting something too heavy with a jerking motion, or abrupt movements.
- Degenerative Changes: Age-related wear and tear, poor posture, or chronic conditions can lead to rotator cuff injuries over time.
Seeking Medical Attention and Diagnosis
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience shoulder joint pain, weakness, or limited range of motion, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further damage.
Diagnostic Process
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will assess your shoulder for tenderness, range of motion, and strength.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays: Used to identify bone spurs or other skeletal issues.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging(MRI): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, helping to identify the extent of tendon damage or tears.
- Ultrasound: Allows real-time visualisation of the rotator cuff tendons.
Incorporating Peptides into Rotator Cuff Injury Treatment
Types of Peptides
- BPC-157: Known for its powerful healing properties, BPC-157 promotes tissue repair and reduces inflammation.
- TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4): Another peptide that aids in healing and has strong anti-inflammatory effects.
Potential Benefits of Peptide Therapy
- Enhanced Healing: Peptides like BPC-157 and TB-500 can accelerate the healing process of injured tissues.
- Reduced Inflammation: They help in significantly reducing inflammation and pain.
- Improved Recovery Time: These peptides can shorten the recovery period, enabling quicker return to activities.
How to Use Peptides
- Consultation with a Healthcare Provider: Always seek professional advice before starting peptide therapy.
- Dosage and Administration: Follow the prescribed dosage and administration guidelines. Peptides are typically administered through subcutaneous injections.
- Monitoring Progress: Regular follow-ups are essential to assess the effectiveness and make necessary adjustments to the treatment.
Preventive Measures for Avoiding Rotator Cuff Injuries

Tips for Prevention
- Proper Technique: Ensure you use proper techniques during sports and exercises to avoid unnecessary strain on your rotator cuff muscles and shoulder.
- Strengthening Exercises: Incorporate exercises that strengthen the rotator cuff and shoulder muscles into your routine. Example exercises include shoulder presses, internal and external rotations, and resistance band workouts.
- Flexibility Exercises: Regular stretching helps maintain the flexibility of shoulder muscles and tendons.
- Posture: Good posture reduces strain on the shoulder.
- Gradual Progression: Gradually increase the intensity of activities to avoid overuse injuries.
- Regular Breaks: Take breaks during repetitive activities to allow muscles and tendons to recover.
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Always warm up before and cool down after physical activities to prepare your muscles and tendons for exertion.
Conclusion
Managing the symptoms of a rotator cuff injury involves a comprehensive approach, from accurate diagnosis and innovative treatments like peptide therapy to preventive measures that ensure long-term shoulder health. By consulting with healthcare professionals, adhering to prescribed treatments, and maintaining a routine of strengthening and flexibility exercises, you can effectively treat and prevent rotator cuff injuries, ensuring a healthy and active lifestyle.


 is here! Shop now, pay later in 4 easy installments
is here! Shop now, pay later in 4 easy installments













